Embark on a journey through time as we explore the Top 10 Ancient Trade Routes that shaped our world. These historic pathways, traversing vast deserts, perilous seas, and rugged mountains, were not just conduits for commodities but catalysts for cultural exchange, technological innovation, and the forging of civilizations. From the bustling Silk Road to the treacherous Tea Horse Road, each route tells a story of human endeavor, resilience, and the unquenchable thirst for exploration and connection. Join us as we unveil the profound impacts these ancient routes had on the course of history, commerce, and cultural development across continents.
10- The Frankincense Trail
Photo Credit: Evidence Central
The Frankincense Trail, a vital artery of commerce from around 300 B.C. to A.D. 300, spanned the Arabian Peninsula, connecting the Mediterranean world with the rich sources of frankincense and myrrh in the southern Arabian Peninsula and the Horn of Africa. These aromatic resins, coveted for religious ceremonies and as luxury items, were among the most prized commodities of the ancient world. The trade along this route not only brought immense wealth to the cities like Petra in Jordan, fostering their development into bustling centers of commerce and culture, but also facilitated significant cultural and religious exchanges between the Mediterranean and the Arabian world.
The prosperity generated by this trade is evident in the architectural marvels of the Nabatean Kingdom, many of which endure to this day, standing as testaments to the historical significance of this route. Moreover, the Frankincense Trail’s impact extended beyond commerce, influencing religious practices and cultural exchanges across the regions it connected.
9- The Amber Road
Photo Credit: Alchetron
The Amber Road, a significant ancient trade network, originated around 3000 B.C. It was essential for transporting amber from the Baltic Sea region to the Mediterranean and further. This route was not just a means for trading amber, a commodity prized for its beauty and supposed magical properties. It also facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural practices between Northern and Southern Europe. This interaction had a profound impact on the economic and cultural landscapes of these regions.
The Amber Road’s influence is evident in the rise of affluent city-states and trade centers along its path, fueled by the wealth from the amber trade. This route demonstrates how a single commodity can shape the development of diverse cultures and economies, highlighting the interconnectedness of ancient civilizations through commerce. The Amber Road was more than a mere trade route; it served as a conduit for cultural exchange and a catalyst for economic development. It linked distant communities, fostering a shared history that continues to resonate in the present day.
8- The Tea Horse Road

Active primarily during the Tang Dynasty (618-907 A.D.), the Tea Horse Road was an extensive network of paths winding through the mountains of Southwest China into Tibet. This route was central to the exchange of Chinese tea for Tibetan horses, which were crucial for China’s military strength. The trade along this route had profound cultural implications, facilitating the spread of Buddhism from India to China and vice versa. Additionally, the route contributed significantly to the economic and cultural development of minority ethnic groups in these regions.
The Tea Horse Road exemplifies the importance of trade in not just economic terms but also in its ability to foster deep cultural and religious connections across diverse communities. The exchange of tea and horses was more than a mere commercial activity; it was a vital link that brought together disparate cultures, allowing for a rich intermingling of traditions, ideas, and beliefs. This route, often treacherous and challenging, was traversed by countless traders and pilgrims, each contributing to the rich tapestry of cultural exchange that defined this ancient pathway.
7- Trans-Saharan Trade Routes

Spanning from the 8th to the 16th centuries, the Trans-Saharan Trade Routes connected North Africa with sub-Saharan Africa, bridging geographical and cultural divides. These routes were instrumental in the exchange of gold, salt, and other precious commodities, playing a crucial role in the economic and cultural development of the regions they connected. The gold from West Africa, in particular, was highly valued in the Mediterranean and European markets, contributing to the wealth and power of West African empires like Mali and Songhai.
Furthermore, these trade routes facilitated the spread of Islam and the Arabic language across the Sahara, significantly impacting the cultural and religious landscape of West Africa. The Trans-Saharan Trade Routes were not merely conduits for goods; they were channels for the exchange of ideas, technologies, and beliefs. The impact of these routes is evident in the rich cultural heritage of the Saharan and sub-Saharan regions, where traditions and customs from different worlds merged and evolved. The legacy of these routes continues to shape the cultural and historical narratives of the regions they once connected, underscoring the enduring influence of ancient trade networks on the course of human history.
6- The Silk Road
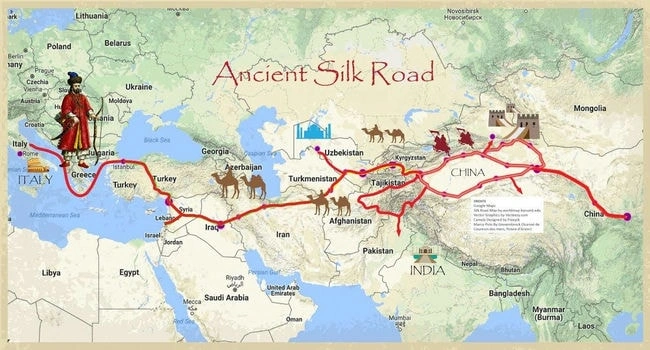
Photo Credit: Medium
The Silk Road, an intricate network of trade routes connecting East Asia with the Mediterranean, stands as one of history’s most significant trade pathways. Active from around the 2nd century B.C. until the 14th century A.D., it facilitated not just the trade of silk but also a myriad of other goods, including spices, grains, fruits, and valuable stones. The Silk Road’s impact on the civilizations it connected was profound, leading to unprecedented levels of cultural, religious, and technological exchanges. It played a crucial role in the spread of Buddhism, Christianity, and Islam, and was instrumental in the transmission of inventions like papermaking and gunpowder.
The Silk Road was more than a commercial route; it was a bridge between worlds, bringing together the diverse cultures of Asia, the Middle East, and Europe. The exchange of goods along this route was paralleled by an exchange of ideas, art, and science, fostering a period of enlightenment and progress that shaped the course of human history. The legacy of the Silk Road is a testament to the power of trade to transcend mere economic transactions, becoming a catalyst for cultural evolution and mutual understanding among disparate civilizations.
5- The Incense Route
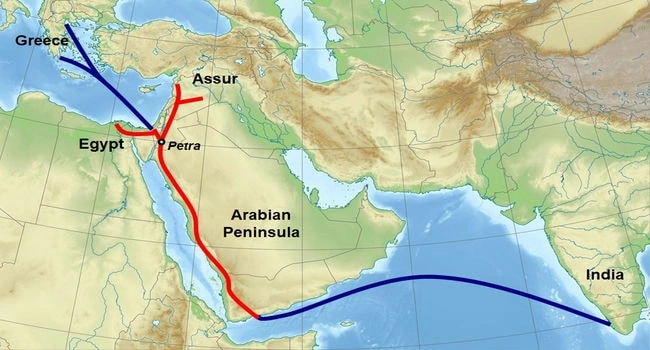
The Incense Route, flourishing from the 7th century B.C. to the 2nd century A.D., was a network of trade paths extending from the Arabian Peninsula to the Mediterranean, primarily used for transporting incense and spices. This route was crucial for the economies of ancient South Arabia and the Mediterranean civilizations, including the Greeks and Romans. The trade of incense, particularly frankincense and myrrh, was not only lucrative but also had significant religious and cultural importance. The Incense Route facilitated the rise of ancient cities like Petra and Palmyra, which became wealthy and influential due to their strategic positions along the route.
Additionally, this trade network played a vital role in cultural exchanges, contributing to the spread of languages, art, and religious practices across the regions it connected. The Incense Route’s impact on the ancient world was substantial, shaping the economic, cultural, and religious landscapes of the civilizations it touched. The prosperity and cultural richness of the cities along this route are enduring reminders of the transformative power of trade in the ancient world.
4- The Spice Route

The Spice Route, prominent from ancient times until the 15th century, was a maritime route linking the East Indies with the Mediterranean and Europe. This route was primarily used for the trade of spices such as pepper, cloves, nutmeg, and cinnamon, which were highly prized in Europe for their flavor and purported medicinal properties. The Spice Route played a significant role in the global economy of the time, driving the exploration and maritime advancements of European powers like Portugal and Spain.
The demand for spices not only fueled the Age of Discovery but also led to the establishment of colonial empires and the opening of new trade markets. The cultural impact of the Spice Route was profound, as it facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and culinary traditions between East and West.The legacy of the Spice Route is evident in the continued fascination and demand for exotic spices, which have become an integral part of global cuisine and culture.
3- The Via Maris
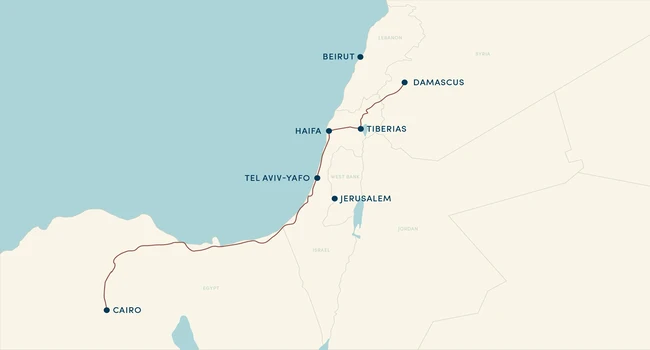
Photo Credit: Via Maris
The Via Maris, an ancient trade route, played a crucial role in the economic, cultural, and political interactions of the civilizations in the Fertile Crescent. Dating back to the early Bronze Age, this route connected Egypt with the northern empires of Syria, Anatolia, and Mesopotamia. Its name, meaning “Way of the Sea” in Latin, reflects its path along the Mediterranean coast. The Via Maris served as a vital corridor for the exchange of goods, ideas, and innovations, linking the ancient Egyptians with the cultures of the Levant and Mesopotamia.
This route facilitated the trade of Egyptian grain, Mesopotamian spices, and luxury goods like silk and precious metals. Additionally, it played a significant role in the military campaigns of ancient empires, as controlling this route meant dominance over the region’s trade and resources. The Via Maris not only highlights the importance of geographical location in trade but also illustrates how trade routes can influence the rise and fall of civilizations by controlling the flow of resources and wealth.
2- The Royal Road
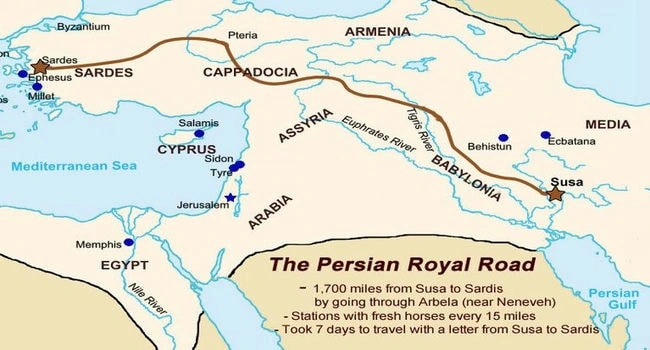
The Royal Road was an ancient highway reorganized and rebuilt by the Persian king Darius the Great of the Achaemenid Empire in the 5th century B.C. This road was an engineering marvel of its time, stretching over 2,000 miles (about 3,200 kilometers) and connecting Susa, the Persian capital, to Sardis near the Aegean Sea. The Royal Road facilitated rapid communication and trade throughout the vast Persian Empire, which stretched from Asia Minor to the Indus River. It was equipped with posting stations at regular intervals, where mounted couriers could exchange horses to deliver messages quickly across the empire.
This system, often compared to a primitive version of the pony express, significantly enhanced the efficiency of communication and governance. The Royal Road also played a crucial role in promoting trade and cultural exchange, allowing for the movement of goods, people, and ideas across diverse regions within the empire. The route’s strategic importance and influence on trade and communication highlight the role of infrastructure in the expansion and maintenance of empires.
1- Maritime Silk Road
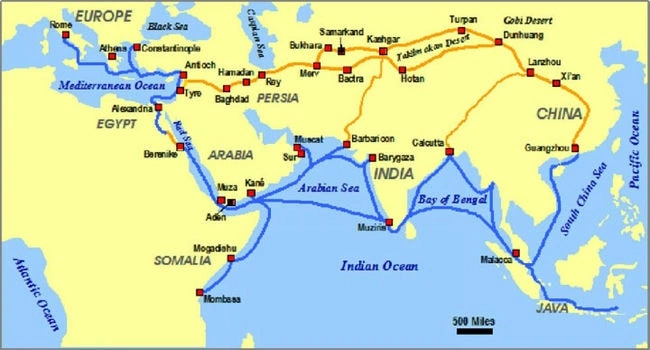
Photo Credit: The Hands India
The Maritime Silk Road, active from around the 2nd century B.C. to the 15th century A.D., was a critical sea route connecting the East with the West. This route extended from the coastal regions of China through Southeast Asia, the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian Peninsula, and into the Mediterranean. The Maritime Silk Road was pivotal for the trade of silk, spices, ceramics, and other luxury goods. It played a significant role in shaping the economies and cultures of the regions it connected, facilitating not only the exchange of goods but also of ideas, technologies, and religions.
The route contributed to the spread of Buddhism, Islam, and other religions along its path, and was instrumental in the cultural and technological exchanges that defined the medieval world. The Maritime Silk Road was a testament to the ingenuity and adventurous spirit of ancient mariners and traders, who braved vast and unpredictable oceans to connect distant lands. The legacy of this route is evident in the rich cultural and historical tapestry of the coastal regions it connected, highlighting the enduring impact of maritime trade on the course of human history.


